On Monday, 16th June 2025, The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) launches its annual assessment of the state of armaments, disarmament and international security. Key findings of SIPRI Yearbook 2025 are that a dangerous new nuclear arms race is emerging at a time when arms control regimes are severely weakened.
World’s nuclear arsenals being enlarged and upgraded
Nearly all of the nine nuclear-armed states—the United States, Russia, the United Kingdom, France, China, India, Pakistan, the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (North Korea) and Israel—continued intensive nuclear modernization programmes in 2024, upgrading existing weapons and adding newer versions.
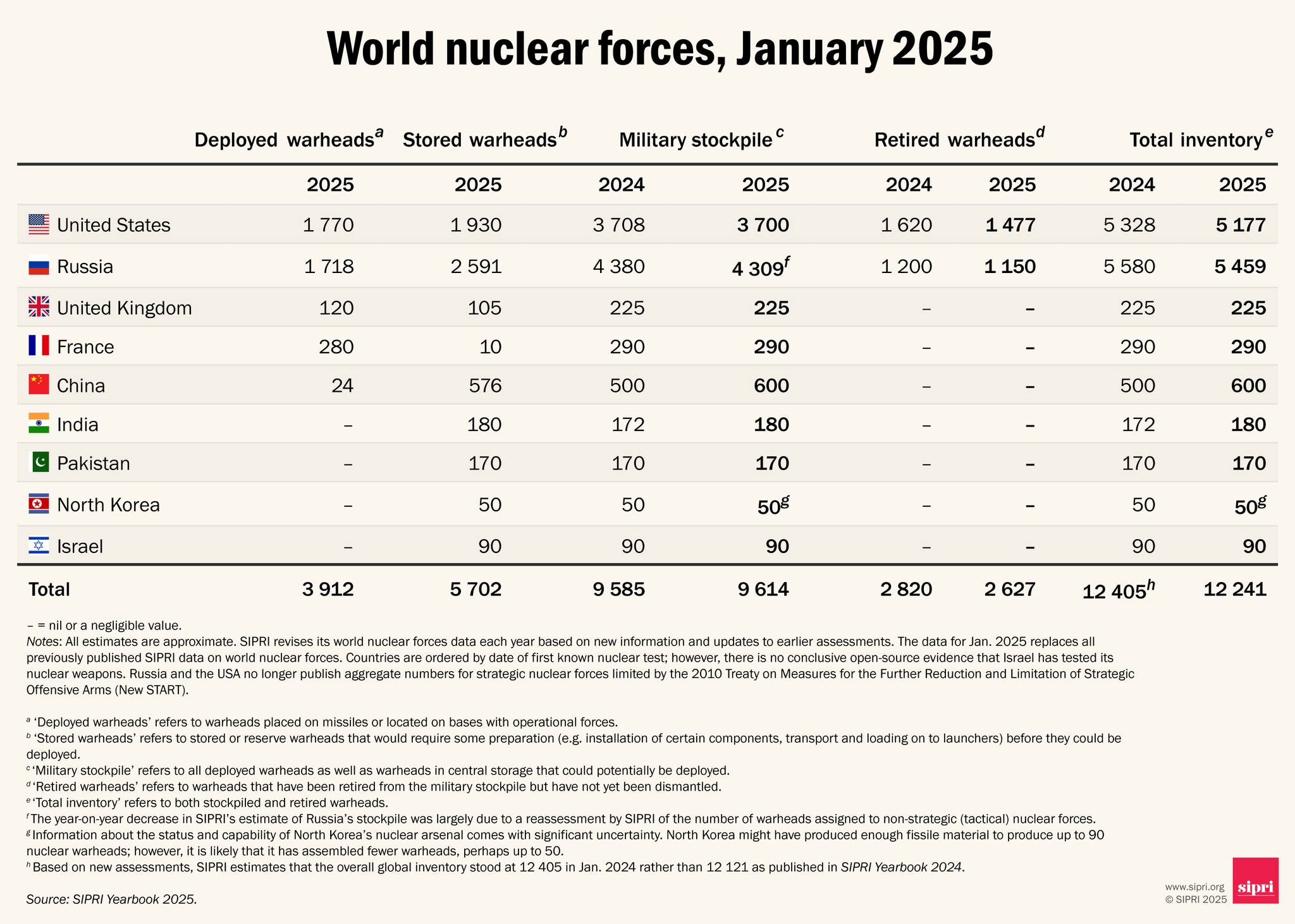
Of the total global inventory of an estimated 12 241 warheads in January 2025, about 9614 were in military stockpiles for potential use (see the table below). An estimated 3912 of those warheads were deployed with missiles and aircraft and the rest were in central storage. Around 2100 of the deployed warheads were kept in a state of high operational alert on ballistic missiles. Nearly all of these warheads belonged to Russia or the USA, but China may now keep some warheads on missiles during peacetime.
Since the end of the cold war, the gradual dismantlement of retired warheads by Russia and the USA has normally outstripped the deployment of new warheads, resulting in an overall year-on-year decrease in the global inventory of nuclear weapons. This trend is likely to be reversed in the coming years, as the pace of dismantlement is slowing, while the deployment of new nuclear weapons is accelerating.
The era of reductions in the number of nuclear weapons in the world, which had lasted since the end of the cold war, is coming to an end, said Hans M. Kristensen, Associate Senior Fellow with SIPRI’s Weapons of Mass Destruction Programme and Director of the Nuclear Information Project at the Federation of American Scientists (FAS). Instead, we see a clear trend of growing nuclear arsenals, sharpened nuclear rhetoric and the abandonment of arms control agreements.
Russia and the USA together possess around 90 per cent of all nuclear weapons. The sizes of their respective military stockpiles (i.e. useable warheads) seem to have stayed relatively stable in 2024 but both states are implementing extensive modernization programmes that could increase the size and diversity of their arsenals in the future. If no new agreement is reached to cap their stockpiles, the number of warheads they deploy on strategic missiles seems likely to increase after the bilateral 2010 Treaty on Measures for the Further Reduction and Limitation of Strategic Offensive Arms (New START) expires in February 2026.
The USA’s comprehensive nuclear modernization programme is progressing but in 2024 faced planning and funding challenges that could delay and significantly increase the cost of the new strategic arsenal. Moreover, the addition of new non-strategic nuclear weapons to the US arsenal will place further stress on the modernization programme.
Russia’s nuclear modernization programme is also facing challenges that in 2024 included a test failure and the further delay of the new Sarmat intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) and slower than expected upgrades of other systems. Furthermore, an increase in Russia’s non-strategic nuclear warheads predicted by the USA in 2020 has so far not materialized.
Nevertheless, it is likely that both Russian and US deployments of nuclear weapons will rise in the years ahead. The Russian increase would mainly happen as a result of modernizing the remaining strategic forces to carry more warheads on each missile and reloading some silos that were emptied in the past. The US increase could happen as a result of more warheads being deployed to existing launchers, empty launchers being reactivated and new non-strategic nuclear weapons being added to the arsenal. Nuclear advocates in the USA are pushing for these steps as a reaction to China’s new nuclear deployments.
SIPRI estimates that China now has at least 600 nuclear warheads. China’s nuclear arsenal is growing faster than any other country’s, by about 100 new warheads a year since 2023. By January 2025, China had completed or was close to completing around 350 new ICBM silos in three large desert fields in the north of the country and three mountainous areas in the east. Depending on how it decides to structure its forces, China could potentially have at least as many ICBMs as either Russia or the USA by the turn of the decade. Yet even if China reaches the maximum projected number of 1500 warheads by 2035, that will still amount to only about one third of each of the current Russian and US nuclear stockpiles.
Although the UK is not thought to have increased its nuclear weapon arsenal in 2024, its warhead stockpile is expected to grow in the future, after the 2023 Integrated Review Refresh confirmed earlier plans to raise the ceiling on warhead numbers. During election campaigning, the Labour government elected in July 2024 declared its commitment to continuing to build four new nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs), maintaining the UK’s continuous at-sea nuclear deterrence, and delivering ‘all the needed upgrades’ to the UK’s nuclear arsenal in future. However, the government now faces significant operational and financial challenges.
In 2024 France continued its programmes to develop a third-generation SSBN and a new air-launched cruise missile, as well as to refurbish and upgrade existing systems, including an improved ballistic missile with a new warhead modification.
India is believed to have once again slightly expanded its nuclear arsenal in 2024 and continued to develop new types of nuclear delivery system. India’s new ‘canisterized’ missiles, which can be transported with mated warheads, may be capable of carrying nuclear warheads during peacetime, and possibly even multiple warheads on each missile, once they become operational. Pakistan also continued to develop new delivery systems and accumulate fissile material in 2024, suggesting that its nuclear arsenal might expand over the coming decade.
In early 2025 tensions between India and Pakistan briefly spilled over into armed conflict.
The combination of strikes on nuclear-related military infrastructure and third-party disinformation risked turning a conventional conflict into a nuclear crisis, said Matt Korda, Associate Senior Researcher with SIPRI’s Weapons of Mass Destruction Programme and Associate Director for the Nuclear Information Project at FAS. This should act as a stark warning for states seeking to increase their reliance on nuclear weapons.
North Korea continues to prioritize its military nuclear programme as a central element of its national security strategy. SIPRI estimates that the country has now assembled around 50 warheads, possesses enough fissile material to produce up to 40 more warheads and is accelerating the production of further fissile material. South Korean officials warned in July 2024 that North Korea was in the final stages of developing a tactical nuclear weapon. In November 2024 the North Korean leader, Kim Jong Un, called for a limitless expansion of the country’s nuclear programme (Second Test of North Korea’s Hwasong-16Na Hypersonic Missile, North Korean submarine-launched cruise missile and construction of nuclear-powered vessels).
Israel—which does not publicly acknowledge possessing nuclear weapons—is also believed to be modernizing its nuclear arsenal. In 2024 it conducted a test of a missile propulsion system that could be related to its Jericho family of nuclear-capable ballistic missiles. Israel also appears to be upgrading its plutonium production reactor site at Dimona.
Arms control in crisis amid new arms race
In his introduction to SIPRI Yearbook 2025, SIPRI Director Dan Smith warns about the challenges facing nuclear arms control and the prospects of a new nuclear arms race.
Smith observes that bilateral nuclear arms control between Russia and the USA entered crisis some years ago and is now almost over. While New START—the last remaining nuclear arms control treaty limiting Russian and US strategic nuclear forces—remains in force until early 2026, there are no signs of negotiations to renew or replace it, or that either side wants to do so. US President Donald J. Trump insisted during his first term and has now repeated that any future deal should also include limits on China’s nuclear arsenal—something that would add a new layer of complexity to already difficult negotiations.
Smith also issues a stark warning about the risks of a new nuclear arms race: The signs are that a new arms race is gearing up that carries much more risk and uncertainty than the last one. The rapid development and application of an array of technologies—for example in the fields of artificial intelligence (AI), cyber capabilities, space assets, missile defence and quantum—are radically redefining nuclear capabilities, deterrence and defence, and thus creating potential sources of instability. Advances in missile defence and the oceanic deployment of quantum technology could ultimately have an impact on the vulnerability of key elements of states’ nuclear arsenals.
Furthermore, as AI and other technologies speed up decision making in crises, there is a higher risk of a nuclear conflict breaking out as a result of miscommunication, misunderstanding or technical accident.
Smith argues that, with all these new technologies and variables in play, the idea of who is ahead in the arms race will be even more elusive and intangible than it was last time round. In this context, the old largely numerical formulas of arms control will no longer suffice.
 Launch of the Russian intercontinental ballistic missile RS-24 Yars / Photo: Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation
Launch of the Russian intercontinental ballistic missile RS-24 Yars / Photo: Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation
More states considering developing or hosting nuclear weapons
Revitalized national debates in East Asia, Europe and the Middle East about nuclear status and strategy suggest there is some potential for more states to develop their own nuclear weapons.
In addition, there has been renewed attention on nuclear-sharing arrangements. In 2024 both Belarus and Russia repeated their claims that Russia has deployed nuclear weapons on Belarusian territory, while several European NATO members signalled their willingness to host US nuclear weapons on their soil, and France’s President Emmanuel Macron repeated statements that France’s nuclear deterrent should have a European dimension (France is considering deploying Rafale jets with nuclear weapons in Germany,
It is critical to remember that nuclear weapons do not guarantee security, said Korda. As the recent flare-up of hostilities in India and Pakistan amply demonstrated, nuclear weapons do not prevent conflict. They also come with immense risks of escalation and catastrophic miscalculation—particularly when disinformation is rife—and may end up making a country’s population less safe, not more.
Global security and stability in growing peril
The 56th edition of the SIPRI Yearbook analyses the continuing deterioration of global security over the past year. The wars in Ukraine, Gaza and elsewhere continued, exacerbating geopolitical divisions, besides their terrible human costs. Furthermore, the election of Donald Trump has created additional uncertainty—in Europe but also further afield—about the future direction of US foreign policy and the reliability of the USA as an ally, a donor or an economic partner.
In addition to the usual detailed coverage of nuclear arms control, disarmament and non-proliferation issues, the SIPRI Yearbook presents data and analysis on developments in world military expenditure, international arms transfers, arms production, multilateral peace operations, armed conflicts, cyber and digital threats, space security governance and more.
Full text of the report in English: SIPRI Yearbook 2025.
📢 Nuclear risks grow as new arms race looms—new SIPRI Yearbook out now.
Read the press release 🔗 https://t.co/jZYllYtWl8#SIPRIYearbook #NuclearWeapons #ArmsControl #NuclearRisk #Disarmament #NonProliferation pic.twitter.com/Qh2Gu1rsNv— SIPRI (@SIPRIorg) June 15, 2025
Read also: